On this page
1.1.1 Signs and symptoms of pregnancy
- The first sign of pregnancy is amenorrhea aCitation a.For amenorrhoea (absence of menstrual periods) without other signs of pregnancy, rule out other causes: physiological (breastfeeding), drug-related (e.g. contraceptives up to 3 months after stopping, antipsychotics and corticosteroids), endocrine (e.g. thyroid disorder), psychological, nutritional, etc. combined with a progressive increase in the size of the uterus starting 7 to 8 weeks after the last menstrual period.
- During the first trimester, breast changes (increased size, tenderness, vascularisation and swollen areolas), urinary frequency and transitory nausea/vomiting are common.
- In the second trimester the mother begins to feel foetal movement and, in some cases, uterine contractions. Foetal heart tone can be heard.
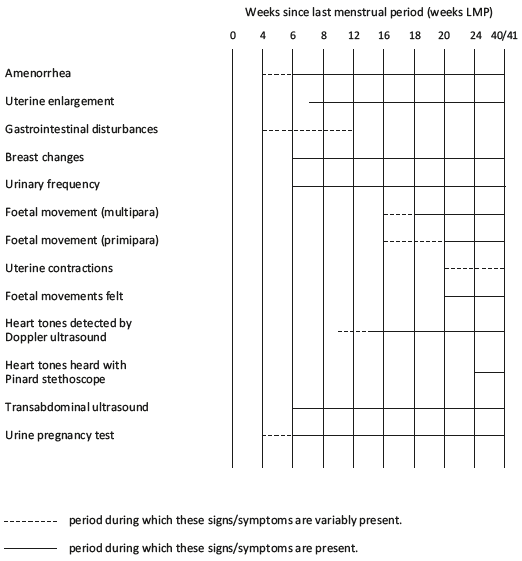
Signs and symptoms of pregnancy by gestational age are presented in the Table 1.1.
Table 1.1 - Signs and symptoms of pregnancy by gestational age
1.1.2 History and clinical examination
See Section 1.2.
1.1.3 Other investigations
Pregnancy test
While a pregnancy test is not routinely necessary, it is indicated for suspected ectopic pregnancy or early diagnosis of a pregnancy to be terminated.
Ultrasound
Ultrasound is not routinely necessary.
Footnotes
- (a)For amenorrhoea (absence of menstrual periods) without other signs of pregnancy, rule out other causes: physiological (breastfeeding), drug-related (e.g. contraceptives up to 3 months after stopping, antipsychotics and corticosteroids), endocrine (e.g. thyroid disorder), psychological, nutritional, etc.