Update: October 2022
16.1 Electrocardiogram (ECG)
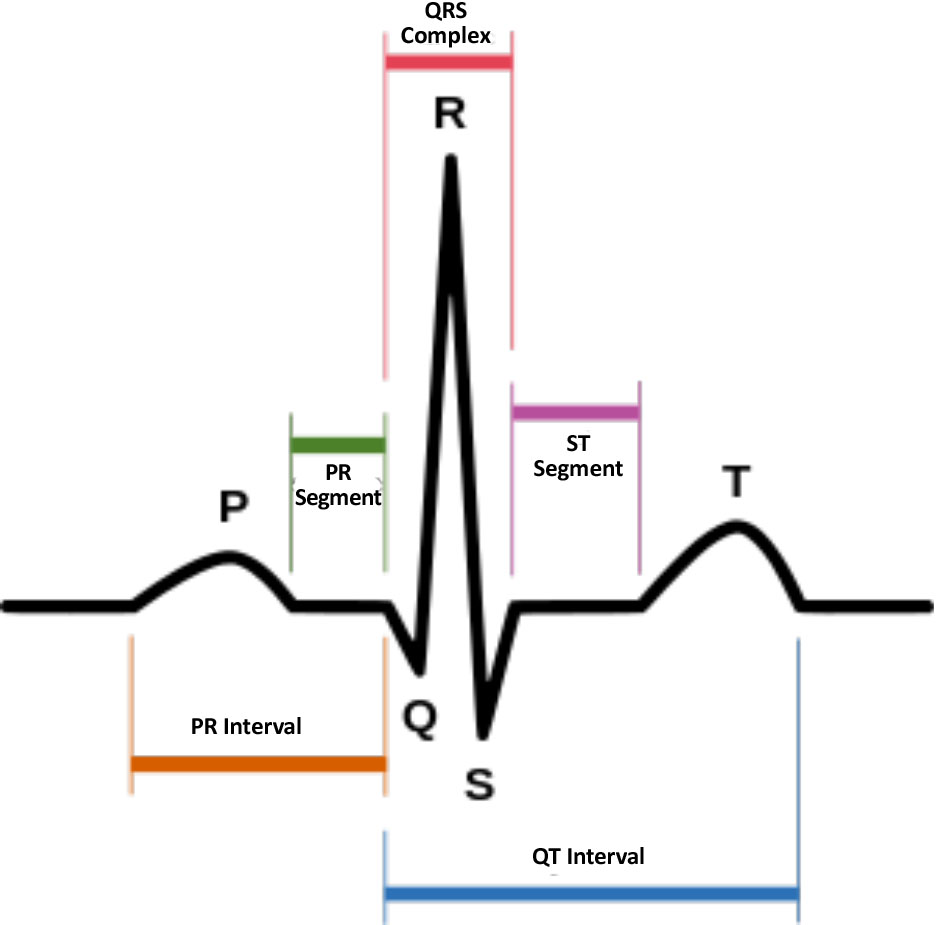
The QT interval is measured in milliseconds (ms) from the start of the QRS complex to the end of the T wave of the ECG. Its value varies depending on the heart rate and should be corrected accordingly (QTc).
To calculate the QTc interval it is recommended to use the Fridericia formula (QTcF) aCitation a.When possible, use a calculator to avoid errors, e.g. https://www.mdcalc.com/corrected-qt-interval-qtc :
QTcF = QT interval divided by cube root of the interval between two waves R
Normal QTc values:
< 470 ms in women
< 450 ms in men
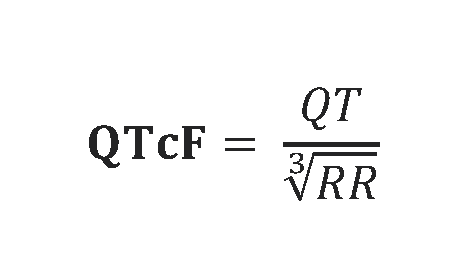
16.2 Brief peripheral neuropathy screen (BPNS)
Adapted from AIDS Clinical Trial Group (ACTG)
[1]Citation 1.Catherine L. Cherry, Steven L. Wesselingh, Luxshimi Lal, Justin C. McArthur. Evaluation of a clinical screening tool for HIV-associated sensory neuropathies. Neurology Dec 2005, 65 (11) 1778-1781.
https://n.neurology.org/content/65/11/1778.long, [2]Citation 2.Mawuntu, Arthur H.P. Mahama, Corry N. et al. Early detection of peripheral neuropathy using stimulated skin wrinkling test in human immunodeficiency virus infected patients;A cross-sectional study. Medicine: July 2018 - Volume 97 - Issue 30.
https://journals.lww.com/md-journal/Fulltext/2018/07270/Early_detection_of_peripheral_neuropathy_using.28.aspx
.
Step 1. Grade subjective symptoms
- Ask the patient to rate the severity of symptoms on a scale from 0 (no symptoms) to 10 (most severe symptoms) for right (R) and left (L) feet and legs.
- Enter the score for each symptom in the corresponding column.
|
Symptoms |
R |
L |
|---|---|---|
|
a. Pain or burning sensation |
|
|
|
b. Pins and needles sensation (tingling sensation) |
|
|
|
c. Numbness (lack of feeling) |
|
|
Symptoms may be unilateral or bilateral and of different intensity. Use the highest subjective sensory neuropathy score to obtain the severity grade.
|
Subjective sensory neuropathy score |
Severity grade |
|---|---|
|
0 |
0 |
|
1-3 |
1 |
|
4-6 |
2 |
|
7-10 |
3 |
Step 2. Evaluate vibration perception
- Place the vibrating 128 Hz tuning fork on the top of the distal joint of the right and left big toes and begin counting the seconds.
- Ask the patient to say when they no longer feel the vibration.
There is a decrease in vibration perception if the patient feels the vibration for 10 seconds or less on both sides.
|
Vibration perception |
Result |
Grade |
|---|---|---|
|
Felt > 10 seconds |
Normal |
0 |
|
Felt 6-10 seconds |
Mild loss |
1 |
|
Felt < 5 seconds |
Moderate loss |
2 |
|
Not felt |
Severe loss |
3 |
Step 3. Evaluate tendon reflexes
Using a reflex hammer, tap the Achilles tendon on each ankle.
Step 4. Make a diagnosis
Diagnosis of peripheral neuropathy is based on the combination of:
- subjective symptoms of grade 1, 2 or 3, and
- at least one bilateral objective finding:
- reduced vibration perception (grade 1, 2 or 3), or
- decreased reflexes (absent or hypoactive reflexes)
16.3 Ishihara test
The patient is asked to look at a set of plates with circles made of dots of different sizes and colours.
Some circles contain dots that form a number or a shape clearly visible to patients with normal colour vision. Patients who cannot see or have difficulty distinguishing numbers or shapes have a red-green colour vision defect.
Some circles contain dots that form a number or a shape visible to patients with red-green colour vision defect, but invisible to patients with normal colour vision.
The test should be performed as per the manufacturer’s instructions.
- (a)When possible, use a calculator to avoid errors, e.g. https://www.mdcalc.com/corrected-qt-interval-qtc
- 1.Catherine L. Cherry, Steven L. Wesselingh, Luxshimi Lal, Justin C. McArthur. Evaluation of a clinical screening tool for HIV-associated sensory neuropathies. Neurology Dec 2005, 65 (11) 1778-1781.
https://n.neurology.org/content/65/11/1778.long - 2.Mawuntu, Arthur H.P. Mahama, Corry N. et al. Early detection of peripheral neuropathy using stimulated skin wrinkling test in human immunodeficiency virus infected patients;A cross-sectional study. Medicine: July 2018 - Volume 97 - Issue 30.
https://journals.lww.com/md-journal/Fulltext/2018/07270/Early_detection_of_peripheral_neuropathy_using.28.aspx