Destructive operation to reduce the volume of a dead foetus to facilitate vaginal delivery when obstruction prevents this from occurring naturally.
There are several types of embryotomy:
- Craniotomy: a procedure in which a perforation is made in the foetal skull to reduce the volume of the foetal head which prevents delivery. It can be done on either an obstructed cephalic presentation or an entrapped aftercoming head in a breech.
- Cranioclasis: a procedure to crush the bones of the foetal skull. It is done if necessary after craniotomy in order to allow extraction of the foetal head.
- Decapitation: a procedure in which the foetus is decapitated to relieve impaction due to a transverse lie.
- Evisceration: a procedure in which an incision is made in the abdomen or thorax in the case of a mass or fluid collection (ascites) which is preventing delivery of the foetus.
- Cleidotomy: a procedure in which one or both clavicles are cut to reduce the biacromial diameter in case of a shoulder dystocia not resolved by other manoeuvres.
Embryotomy, especially as often performed on a fragile and infected uterus, carries the risk of trauma (e.g., uterine rupture, cervical or vaginal injury, and damage to maternal soft tissue with fistula). This risk is especially high in the event of decapitation.
Few people have experience with these procedures. The operators must have the knowledge of obstetrics, must feel comfortable performing obstetric manoeuvres and must have skills to manage potential complications.
Some practitioners would rather perform a caesarean section on a dead foetus than have to mutilate a foetus. However, independently of the mode of delivery (by caesarean section or vaginally), obstructed labour carries a significant risk of puerperal infection, fistula and postpartum haemorrhage. In addition, caesarean section can place the mother at significant risk in terms of both survival and function. The objective of embryotomy is to reduce such risks.
Embryotomy should be performed in a CEmONC facility (refer if necessary, even if the referral takes time).
9.7.1 General conditions and precautions
There is no urgency in extracting the foetus. The priority is maternal intensive care (intravenous line, IV hydration, antibiotic therapy for prolonged rupture of membranes or infection, and urinary catheterisation).
The embryotomy can be performed once the mother is stable, under the following conditions:
- Confirm foetal death: no heart tones on foetal Doppler or ultrasound.
- Confirm the obstacle to vaginal delivery due to size and/or presentation.
- Make sure there is adequate access to the foetus: full or nearly full dilation and ruptured membranes.
- Insert a Foley catheter.
- Perform the procedure in the operating room under strict aseptic conditions and anaesthesia; always prepare for laparotomy in case of uterine rupture.
- Take time to explain to the mother and family the expected benefits (avoiding caesarean section) and potential complications (possible laparotomy if the event of embryotomy failure or uterine rupture). Obtain the patient’s consent.
- After extracting the foetus, routinely check:
- the uterine cavity (uterine exploration with antibiotic prophylaxis, Section 9.3);
- the vaginal walls (use the vaginal retractors in the curettage set, for example, to get adequate exposure).
- After the procedure, routinely administer oxytocin IM or slow IV: 5 IU or 10 IU.
- In the event of obstructed labour, leave the Foley catheter in place for 14 days to reduce the risk of fistula formation.
- Care for the body of the infant: suture the skin wounds; clean and wrap up the infant to show/give him to the parents or family, depending on their choice.
9.7.2 Contra-indications
- Doubt about whether the foetus is dead or alive
- Uterine rupture
- Incomplete dilation
9.7.3 Equipment
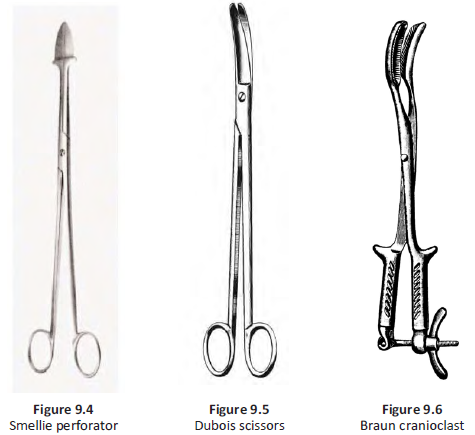
- Smellie perforator (Figure 9.4)
- Dubois scissors or large, curved scissors (Figure 9.5)
- Braun cranioclast (Figure 9.6)
- 4 Faure forceps
9.7.4 Craniotomy for obstructed cephalic presentation
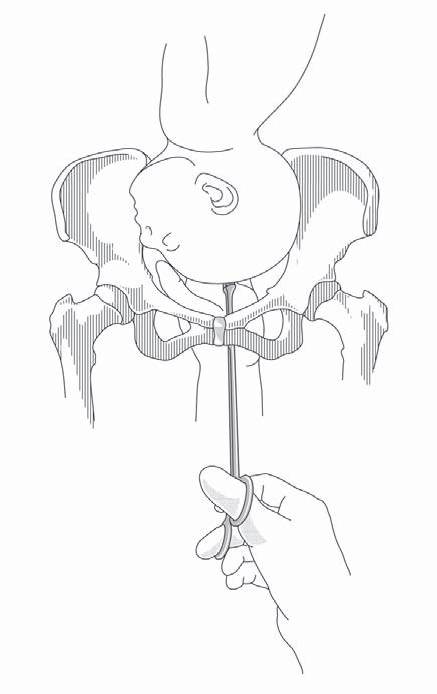
Figure 9.7 - Embryotomy with the Smellie perforator
- Have an assistant place both palms on the mother's abdomen to apply downward pressure on the foetal head toward the pelvis.
- Insert one hand, shaped like a channel, into the vagina, in contact with the foetal head.
- Using the other hand, slide the perforator along the channel formed by the first hand (to protect the vagina) until it makes contact with the foetal head. This can be done under direct vision after retraction with vaginal retractors.
- The perforation should be made in the centre of the skull to protect the mother's soft tissues. It is easier to do it in a fontanelle. Rotate the instrument to make the perforation, and then remove it so that the cerebrospinal fluid and/or brain matter can drain through the hole.
- Once the cerebrospinal fluid spills out, the head should collapse and delivery should be easy; if not, apply traction to the skull with 3 or 4 forceps, gripping the scalp around the perforation. If necessary, perform cranioclasis.
Note: if the foetus is hydrocephalic, perforation can be replaced by needle aspiration.
9.7.5 Cranioclasis
- Insert the cranioclast’s solid jaw into the opening made by the perforator. The hollow jaw is placed beside the skull similar to the placement of obstetric forceps.
- Adjust the two jaws with the screw and extract the head in the most favourable orientation.
9.7.6 Craniotomy for entrapped aftercoming head in a breech
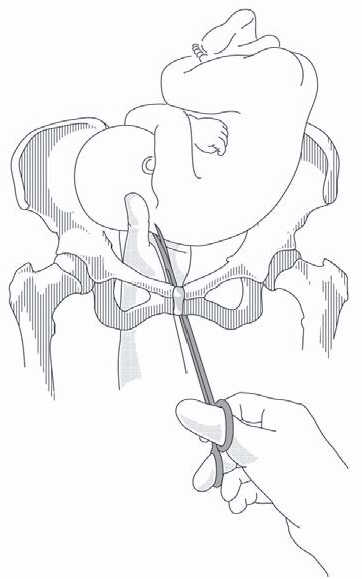
Figure 9.8 - Craniotomy for retention of the aftercoming head
- Have an assistant place both palms n the mother's abdomen to apply downward pressure on the foetal head toward the pelvis.
- Pull the body of the foetus out and down to gain access to the occiput. If necessary, retract the anterior vaginal wall using a vaginal wall retractor.
- Insert the perforator (or scissors, if there is no perforator) under the occiput. Rotate the instrument to make the perforation. Open and close to cut up the contents.
- Remove the perforator and apply traction to the trunk. If the head remains trapped, traction can be applied directly to the skull with forceps attached around the perforation.
Note: if the foetus is hydrocephalic, perforation can be replaced by needle aspiration.
9.7.7 Decapitation for transverse lie
This is the most difficult type of embryotomy to perform, and the one carrying the greatest risk of maternal trauma.
If the foetus is big and/or hard to access, embryotomy cannot be done and caesarean section is the first and only option. Be aware that the caesarean section will be complicated, with potentially difficult foetal extraction and the risk of enlargement of the hysterotomy.
Embryotomy can be attempted if the foetus is small and easy to access. First try internal version (Chapter 7, Section 7.8) in the operating room under anaesthesia and total breech extraction (Chapter 6, Section 6.3), with or without craniotomy.
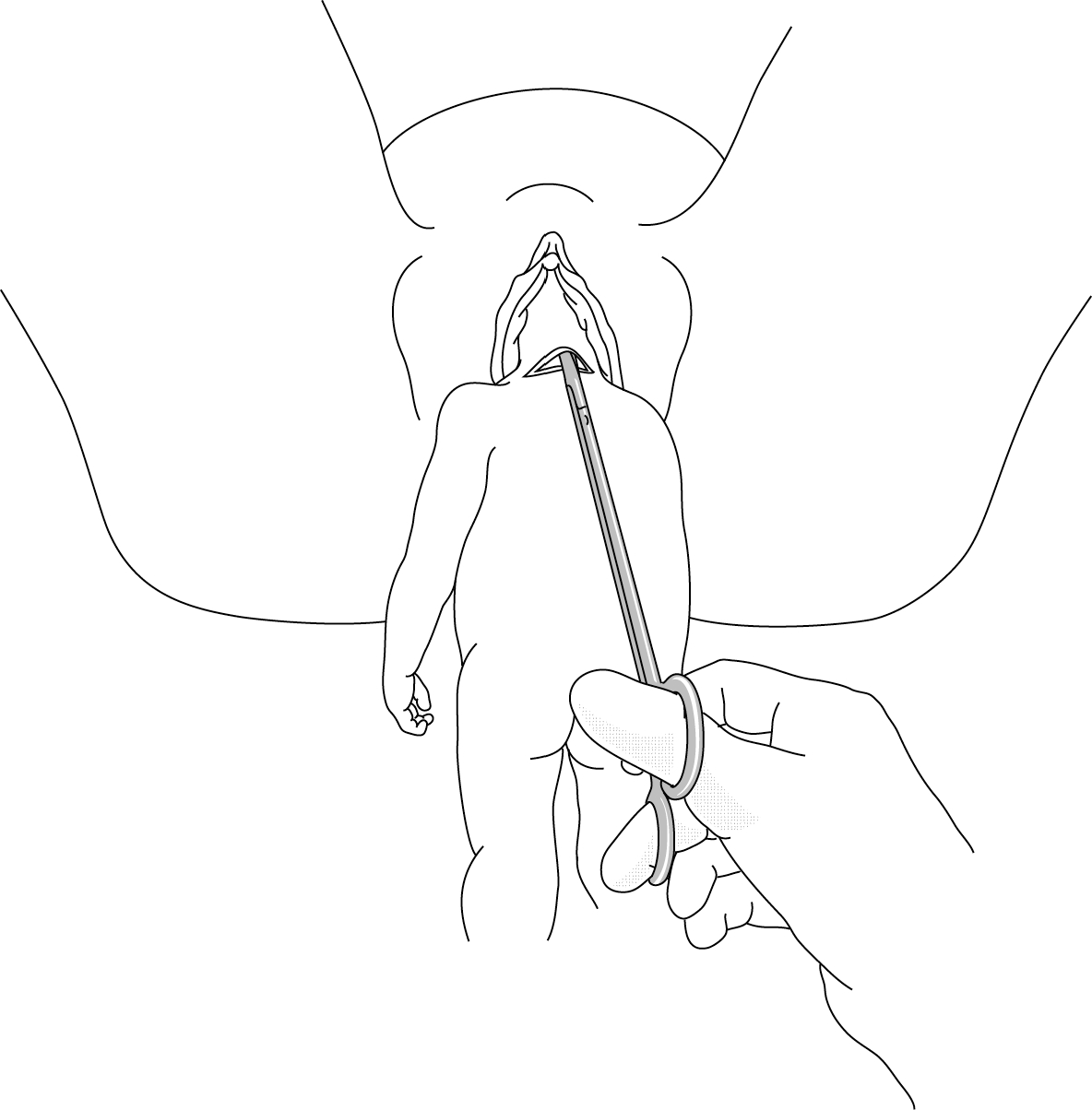
Figure 9.9 - Decapitation using scissors
- Determine the exact position of the foetus (position of the head and neck and which arm is prolapsed.
- In case of neglected shoulder presentation (Chapter 7, Section 7.6.1), have an assistant apply traction to the prolapsed arm (do not try to section the arm first, as it can be used to pull the body downward).
- Slide one hand behind the foetus and surround the neck with thumb and index finger, like a necklace.
- With the other hand, slide the closed scissors into the channel formed by the first hand, keeping them flat against the hand. It is imperative to approach the neck at a right angle.
- Using fingers to control and guide, section the neck bit by bit, in the hollow of the hand, opening the scissor blades only slightly each time.
- After decapitation, bring the arms down one after the other and deliver the body.
- To deliver the head, grasp the neck stump and pull downward, performing the delivery as for retention of the aftercoming head, fingers in the foetus’ mouth.
9.7.8 Evisceration
- Initially, attempt to puncture the abdomen with a needle. This might be sufficient to reduce the foetal ascites to allow delivery.
- In case of failure (either insufficient fluid reduction or a solid mass), use scissors to incise, under vision, the abdominal wall and remove the organs.
9.7.9 Cleidotomy
It is difficult to cut one or both clavicles with Dubois scissors and there is a high risk of cutting maternal tissue. It should not be attempted unless all of the obstetrical manoeuvres described in Chapter 7, Section 7.5.1. have failed after several attempts.