On this page
Therapeutic action
- Local anaesthetic
Indications
- Local anaesthesia:
- minor operations: 1% lidocaine
- dental surgery: 2% lidocaine (plain or with epinephrine)
Forms and strengths, route of administration
- 1% solution in 20 and 50 ml vials (10 mg/ml), for SC infiltration
- 2% solution in 20 and 50 ml vials (20 mg/ml), for SC infiltration
Dosage
- The volume to be injected depends on the surface area to be anesthetised.
- Do not exceed:
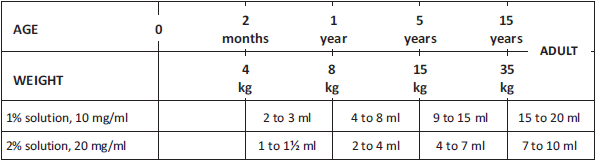
- Child: 5 mg/kg/injection
- Adult: 200 mg = 20 ml of lidocaine 1% or 10 ml of lidocaine 2%
Duration
- One injection, repeated if necessary.
Contra-indications, adverse effects, precautions
- Do not administer if known allergy to lidocaine, impaired cardiac conduction.
- When anaesthetising the extremities, inject distally (at the base), in circle, without tourniquet and without epinephrine (adrenaline).
- Do not use lidocaine for the incision of abscesses: risk of spreading the infection.
- Lidocaine with epinephrine (adrenaline):
- in dental surgery, epinephrine added to lidocaine prolongs anaesthesia;
- never use solutions with epinephrine for the anaesthesia of extremities (fingers, penile nerve block): risk of ischemia and necrosis.
- Pregnancy: no contra-indication
- Breast-feeding: no contra-indication
Remarks
- Anaesthesia is produced within 2 to 5 minutes and lasts 1 to 1.5 hours.
- Do not confuse with lidocaine 5% hyperbaric which is reserved for spinal anaesthesia.
- The more concentrated the lidocaine, the more localised the anaesthetic effect.
- To simplify protocols, use lidocaine 2% with epinephrine for dental anaesthesia and lidocaine 1% without epinephrine for cutaneous anaesthesia.
Storage
– Below 25 °C